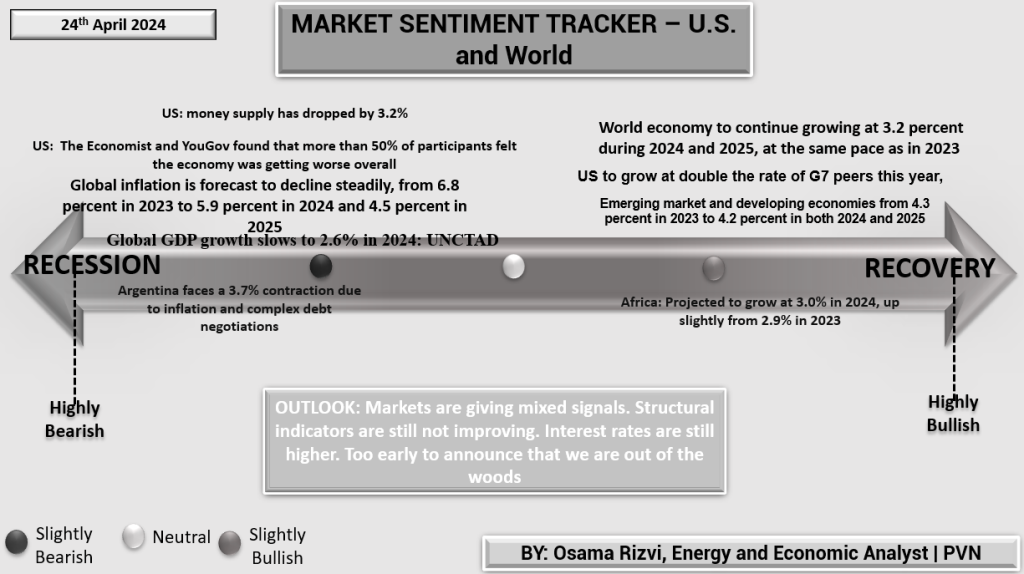
The Market Sentiment Tracker for the U.S. and the world, dated 24th April 2024, portrays a complex global economic environment. The U.S. money supply’s decrease by 3.2% is a significant contraction that may suggest tightening liquidity or a shift in monetary policy. A survey by The Economist and YouGov indicates that over half of respondents perceive a deterioration in the economic situation.
Global GDP growth is decelerating to 2.6% according to UNCTAD, signaling slower economic momentum. This is coupled with a projected easing in global inflation, from 6.8% in 2023 to a more moderate 4.5% by 2025, perhaps reflecting effective monetary interventions or softening demand.
Specific regional highlights include Argentina’s struggle with a 3.7% economic contraction due to inflationary pressures and complex debt negotiations, suggesting significant distress in the country’s financial stability. Meanwhile, Africa shows resilience with a modest growth forecast of 3.0% for 2024.
The recovery section indicates steady global growth at 3.2%, unchanged from the previous year, with the U.S. economy notably outpacing G7 peers. However, emerging markets and developing economies face a slight decrease in growth prospects.
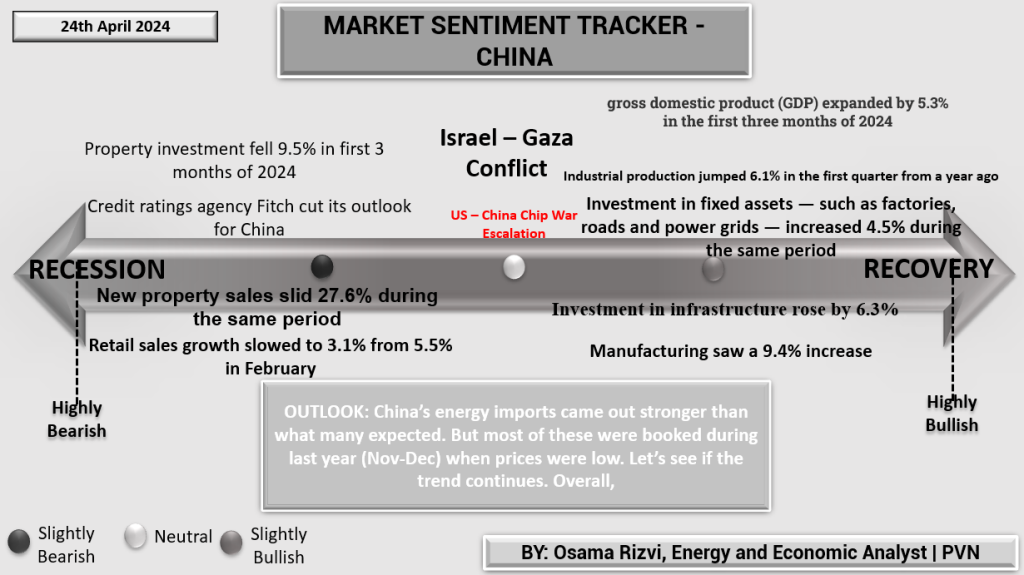
The Market Sentiment Tracker for China dated 24th April 2024 reflects varied economic currents. On one hand, China’s GDP growth remains robust, expanding by 5.3% in the first quarter. This is further supported by a 6.1% increase in industrial production and a substantial 9.4% rise in manufacturing, indicating industrial robustness. Investment in critical infrastructure and fixed assets, such as factories, roads, and power grids, has also seen a positive uptick of 4.5% and 6.3%, respectively.
Conversely, the property sector appears troubled, with investment tumbling 9.5%, and property sales sharply down by 27.6%. This downturn in the property market may be a cause for concern as it could indicate broader economic stresses, including potential issues in credit markets and consumer confidence, which is underscored by retail sales growth decelerating to 3.1% from a healthier 5.5%.
Fitch’s outlook downgrade captures this dichotomy, reflecting the risks facing China amidst a generally strong industrial and manufacturing landscape.
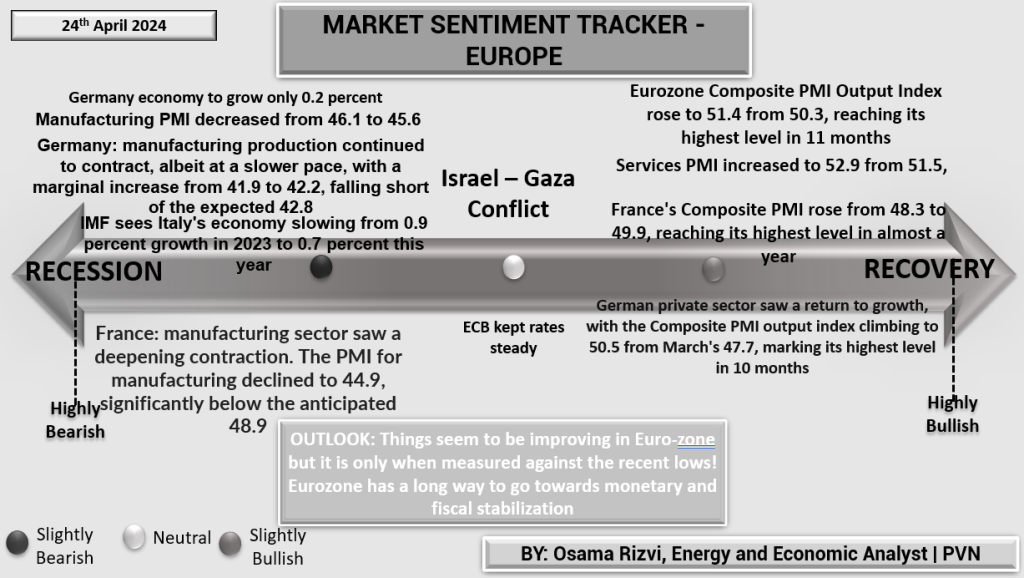
The Market Sentiment Tracker for Europe dated 24th April 2024 presents a mosaic of economic conditions across the region. German economic growth is anemic, expected to be just 0.2%, reflecting broader European challenges. Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) figures underscore these issues, decreasing from 46.1 to 45.6, further evidencing the sector’s contraction. Italy is also witnessing a slowdown, with the IMF projecting a deceleration from 0.9% growth in 2023 to 0.7% in 2024.
France’s manufacturing sector is particularly hard hit, with PMI plummeting to 44.9, well below the neutral 50-point mark that separates expansion from contraction. This is indicative of a deepening industrial recession in one of the Eurozone’s core economies. However, not all indicators are bleak. The Eurozone Composite PMI Output Index has seen a surge to 51.4, the highest in 11 months, signaling overall expansion across manufacturing and services. Similarly, France’s composite figure rose to 49.9, and the German private sector bounced back, with PMI reaching a 10-month high of 50.5.
The current global economic landscape is marked by uneven recovery patterns. The U.S. is exhibiting signs of steady, though moderate, growth with a strong job market overshadowed by inflation concerns. The Eurozone presents a more fragmented picture; while some member states show resilience in manufacturing, others are hindered by declining production figures. In contrast, China’s manufacturing and industrial sectors are expanding, although the real estate sector’s slowdown poses risks to overall stability. These divergent trajectories underscore the ongoing challenge of attaining synchronized global growth, emphasizing the need for adaptive and responsive economic policies across the board.












