The Market Sentiment Tracker provides a nuanced view of the global economy as of May 2024. Economic growth in the United States has decelerated to 1.6%, the lowest in two years, despite the IMF’s recent revision of the US GDP growth forecast upwards to 2.7% for 2024. This disparity highlights ongoing adjustments in the economic outlook influenced by both domestic and global factors.
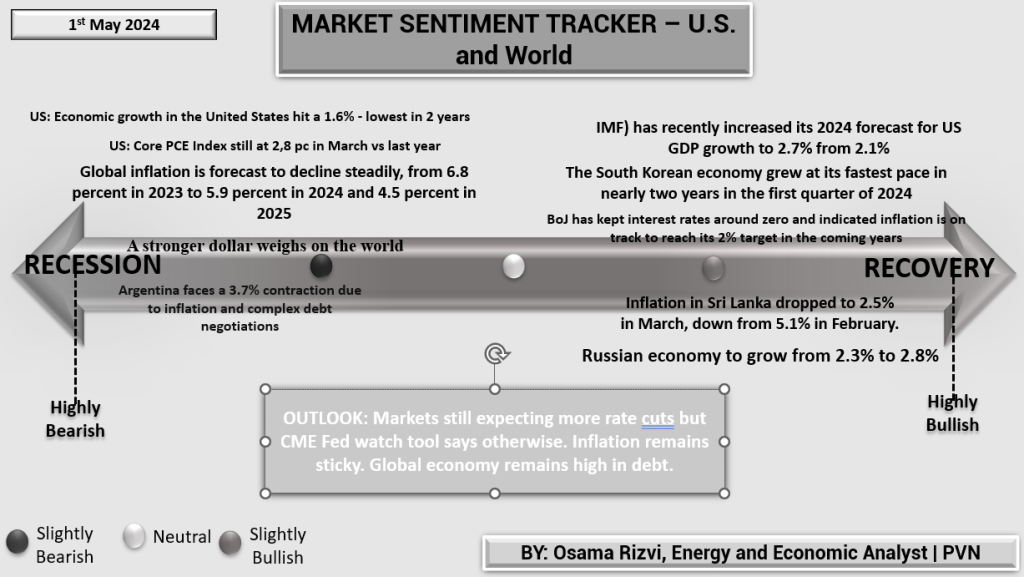
Globally, inflation rates are showing a gradual decline. From a high of 6.8% in 2023, inflation is expected to moderate to 5.9% in 2024 and further to 4.5% by 2025. This trend reflects efforts by central banks worldwide to stabilize prices without throttling growth. In Asia, the economic landscape is mixed. The South Korean economy reports its fastest growth rate in nearly two years during the first quarter of 2024, indicating a robust recovery. Conversely, Japan’s economic policy remains committed to ultra-low interest rates, aiming to secure a long-term inflation target of 2%, suggesting a cautious approach towards monetary tightening. Emerging markets present diverse scenarios: Argentina grapples with a severe 3.7% contraction due to inflation and complex debt negotiations, highlighting the vulnerabilities in economies heavily reliant on external financing. Meanwhile, the Russian economy is projected to improve, with growth expected to rise from 2.3% to 2.8%, signaling some recovery amidst global economic challenges.
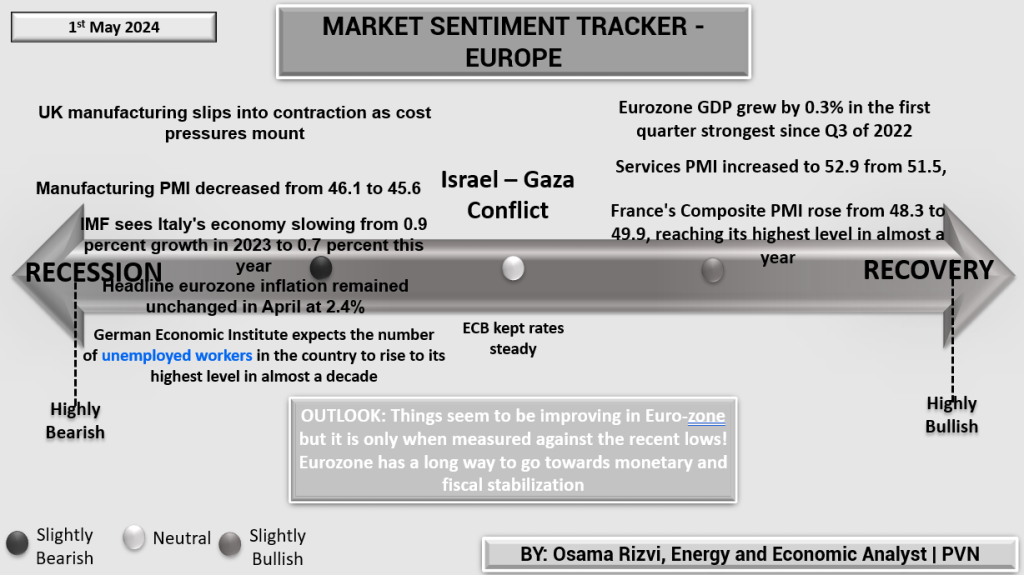
The latest Market Sentiment Tracker for Europe highlights a mixed economic landscape as of May 2024. The region’s manufacturing sector is feeling the strain, notably in the UK where manufacturing has contracted due to escalating cost pressures, driving the Manufacturing PMI down from 46.1 to 45.6. This contraction is part of a broader European trend where economic pressures are intensifying, despite some positive signs.
The Eurozone’s GDP experienced modest growth of 0.3% in the first quarter, marking the strongest quarterly growth since Q3 of 2022. Services sector activity has also shown resilience, with the Services PMI climbing from 51.5 to 52.9. France, in particular, is seeing an improvement, with its Composite PMI increasing to 49.9, nearing expansion territory.
Inflation remains a controlled factor within the Eurozone, stable at 2.4% in April, which suggests that the European Central Bank’s (ECB) policy to hold interest rates steady is currently effective in managing price stability without stifling growth. However, economic challenges persist, as evidenced by Italy’s economic slowdown, with growth projections dipping from 0.9% in 2023 to 0.7% in 2024, and Germany’s rising unemployment projections, signaling potential long-term concerns.
Key takeaways
In analyzing the market sentiment trackers for the U.S. and Europe as of April 2024, we see a contrasting landscape between cautious growth and persistent economic challenges. The U.S. shows a slight uptick in GDP growth forecasts and notable growth in South Korea, indicating some resilience. However, a stronger dollar and high global indebtedness underscore ongoing global economic vulnerabilities that could temper growth prospects.
Europe’s picture is more mixed, with some sectors showing recovery while manufacturing remains hampered by cost pressures. The slight improvements in European services and composite PMIs suggest a gradual stabilization, but the overall pace remains slow, with high unemployment in Germany signaling deeper structural issues.
Both regions reflect a global economy that is walking a tightrope between recovery and existing economic strains, with policy decisions needing to carefully balance growth stimulation against inflation and debt management challenges.












